Using machine learning to classify user comments on GOV.UK
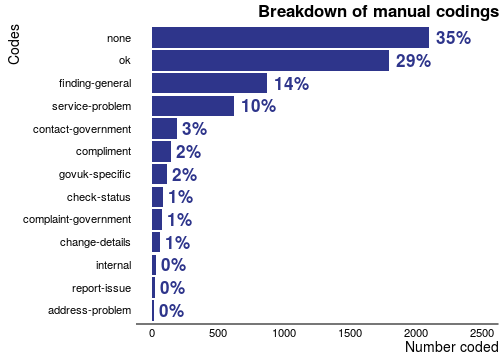
...free text response, for example: 'Why did you visit GOV.UK today?', 'Did you find what you were looking for?', and 'Where did you go for help?'. We receive around 3,000...

...free text response, for example: 'Why did you visit GOV.UK today?', 'Did you find what you were looking for?', and 'Where did you go for help?'. We receive around 3,000...
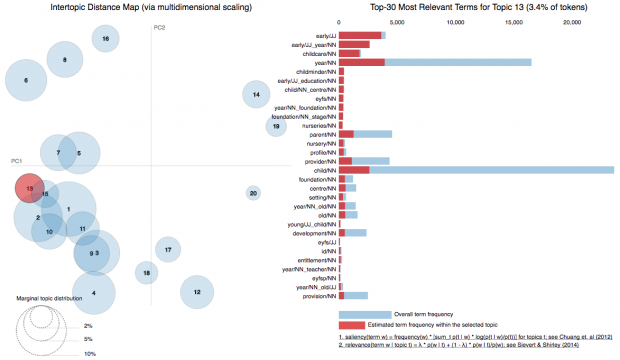
We are creating a single taxonomy for GOV.UK, to make it easier for visitors to find what they are looking for quickly. This blog is about how we have experimented...
...for dealing with an unexpected or malicious incident - a failover page will be available that will direct users to the paper application form. Backups are in place, and pager...
...make it easier for providers and employers to advertise and collaborate on available apprenticeship and trainee roles. User research has shown that both groups have different needs and the service...
...to the team that is responsible for identifying actionable data insights from the service. The assessment panel for the beta assessment recommended that ‘the service team continue in their efforts...
...answer to a question made them ineligible for registration – user research has shown that users prefer to work through the three questions and then be told the reason for...
...as a Digital by Default service. We look forward to seeing what the team will deliver in the future for Self Assessment. The success of the service so far in...
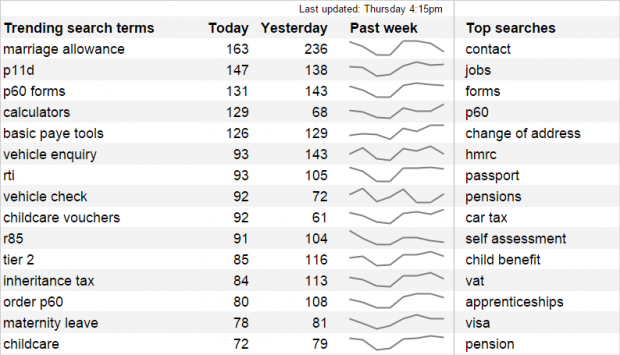
Using Google Analytics and Google Sheets, you can set up a dashboard to see search terms that people are looking for more than usual. By filtering out searches that are...
...This will be needed to ensure that funding is available for appropriate support that meets the standard. The plan for beta sounds reasonable but there is a lot of work...
...or other data collections * is appropriate for some survey methods – for example, a paper survey might have limited space for ethnicity categories This need for concise lists will...